
Radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a surface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅sr −1⋅nm −1. Radiant intensity per unit frequency or wavelength. Radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit solid angle. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅nm −1. Radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength. This is sometimes also called "radiant power", and called luminosity in Astronomy. Radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time. For instance, the irradiance of Alpha Centauri A (radiant flux: 1.5 L ☉, distance: 4.34 ly) is about 2.7 × 10 −8 W/m 2 on Earth. This is a good approximation because the distance from even a nearby star to the Earth is much larger than the star's diameter. In astronomy, stars are routinely treated as point sources even though they are much larger than the Earth. A is the surface area of a sphere of radius r.įor quick approximations, this equation indicates that doubling the distance reduces irradiation to one quarter or similarly, to double irradiation, reduce the distance to 0.7.Irradiance of a surface, denoted E e ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined as E e = ∂ Φ e ∂ A, The two forms have different dimensions and units: spectral irradiance of a frequency spectrum is measured in watts per square metre per hertz (W⋅m −2⋅Hz −1), while spectral irradiance of a wavelength spectrum is measured in watts per square metre per metre (W⋅m −3), or more commonly watts per square metre per nanometre (W⋅m −2⋅nm −1). Spectral irradiance is the irradiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. In astrophysics, irradiance is called radiant flux. Irradiance is often called intensity, but this term is avoided in radiometry where such usage leads to confusion with radiant intensity. The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm −2⋅s −1) is often used in astronomy.
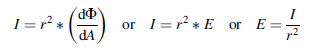
The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m −2). In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux received by a surface per unit area.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
